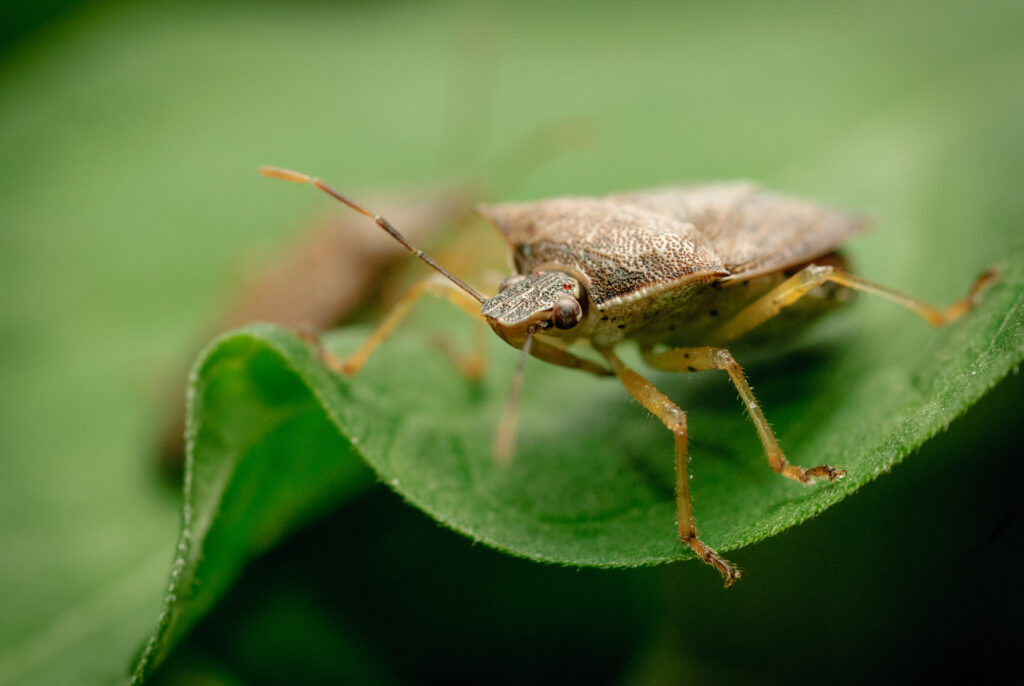
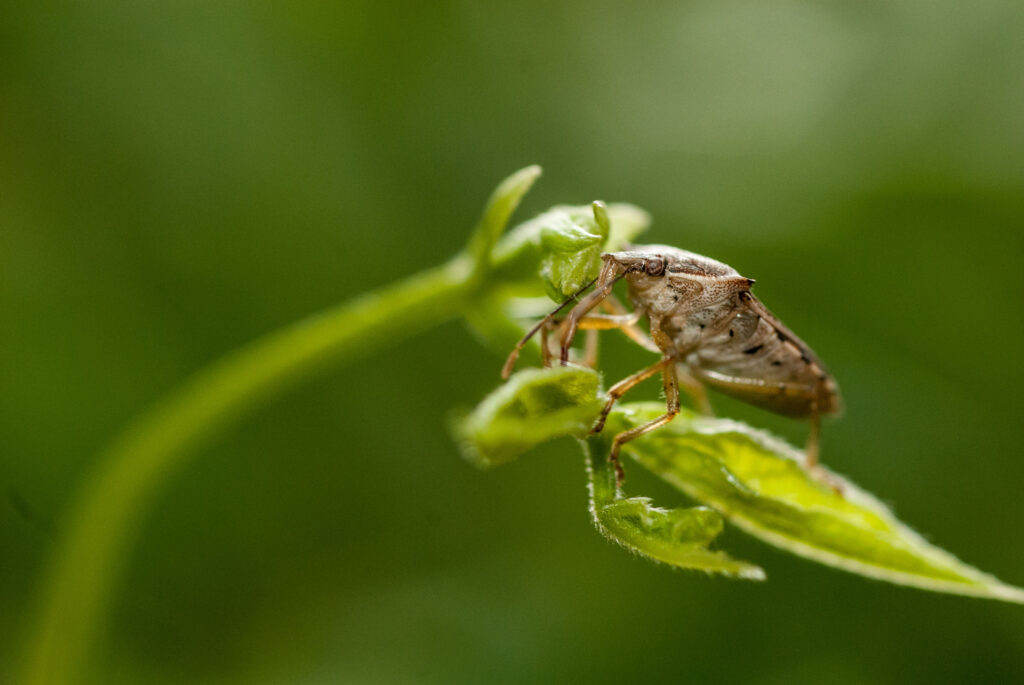
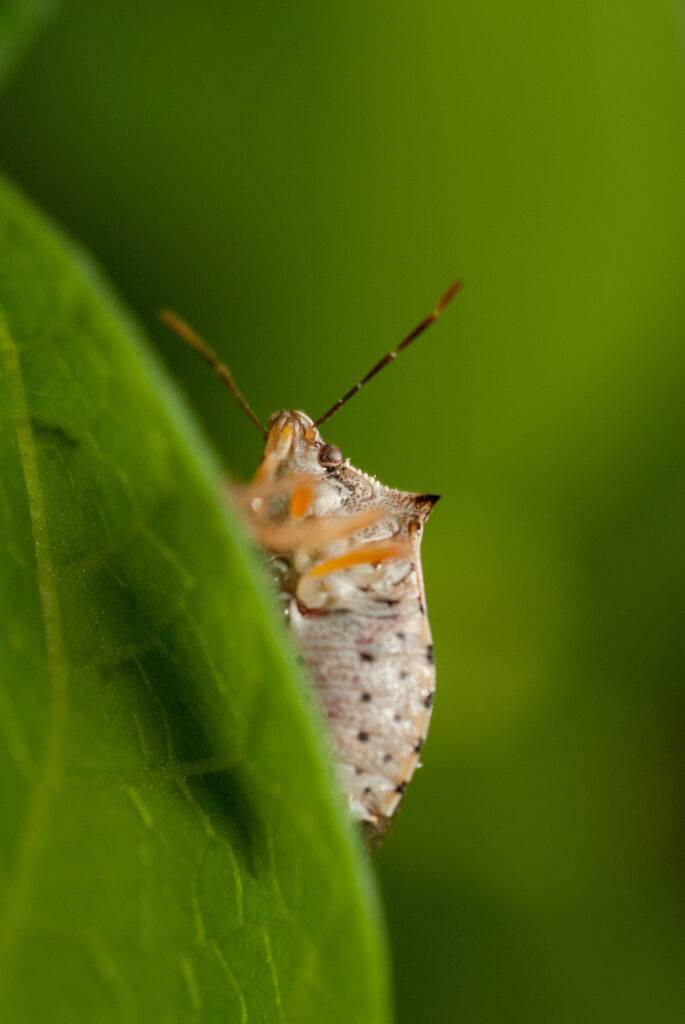
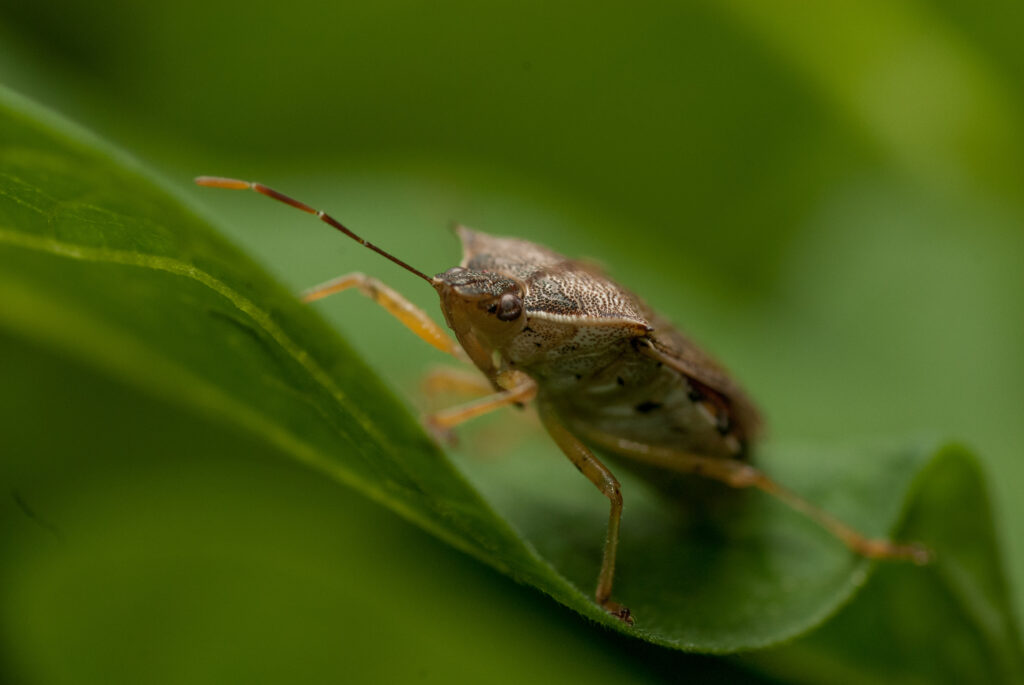
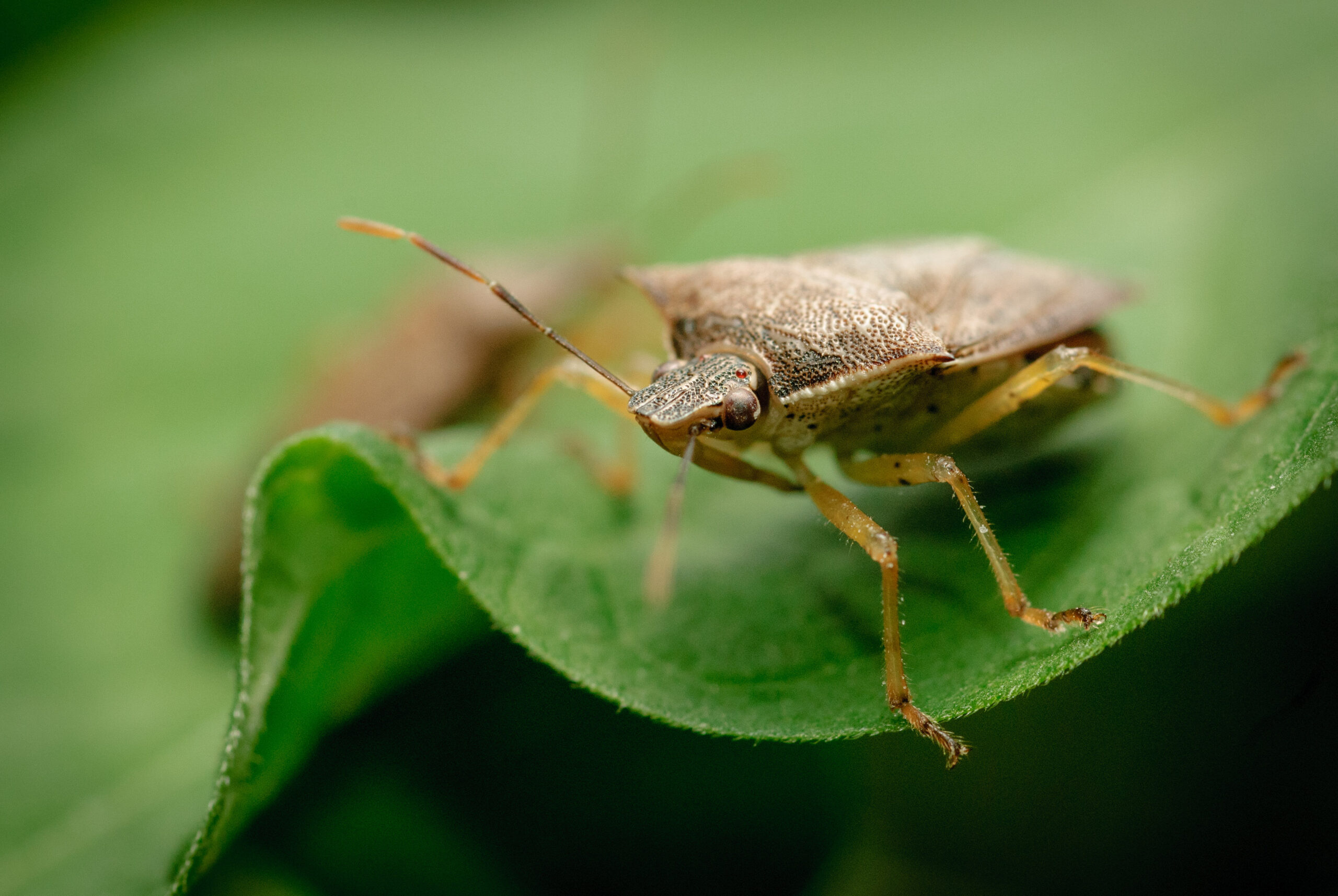
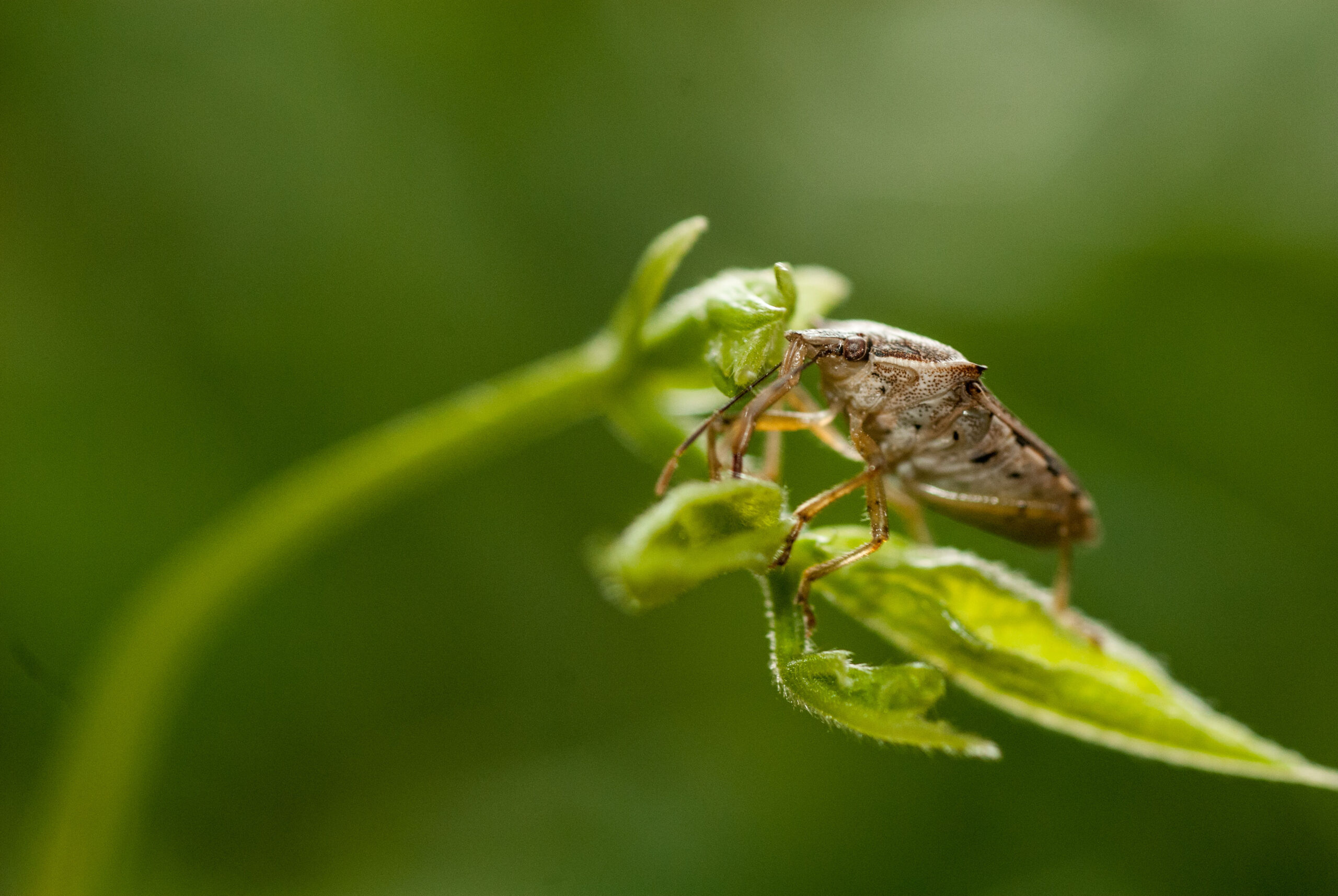
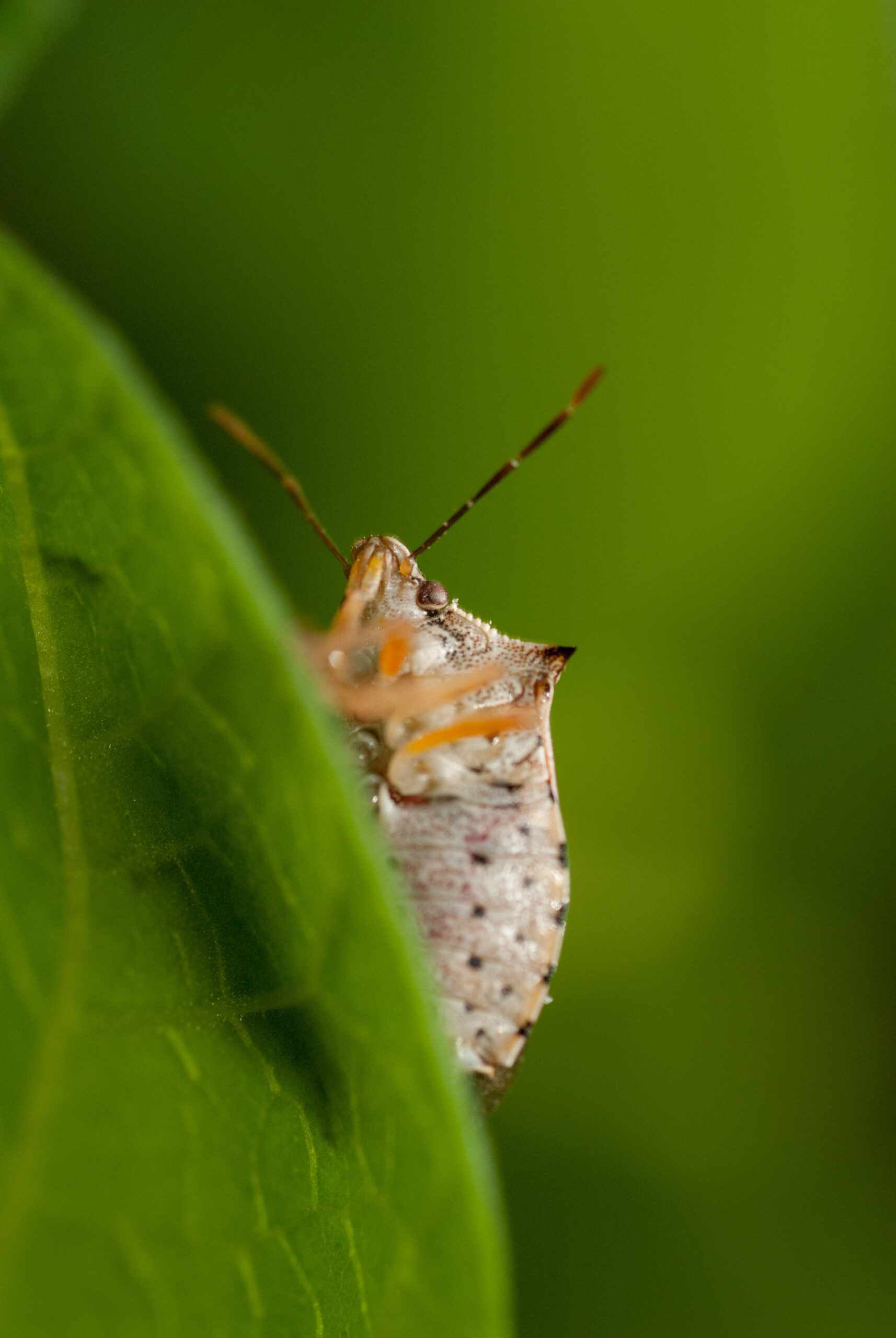
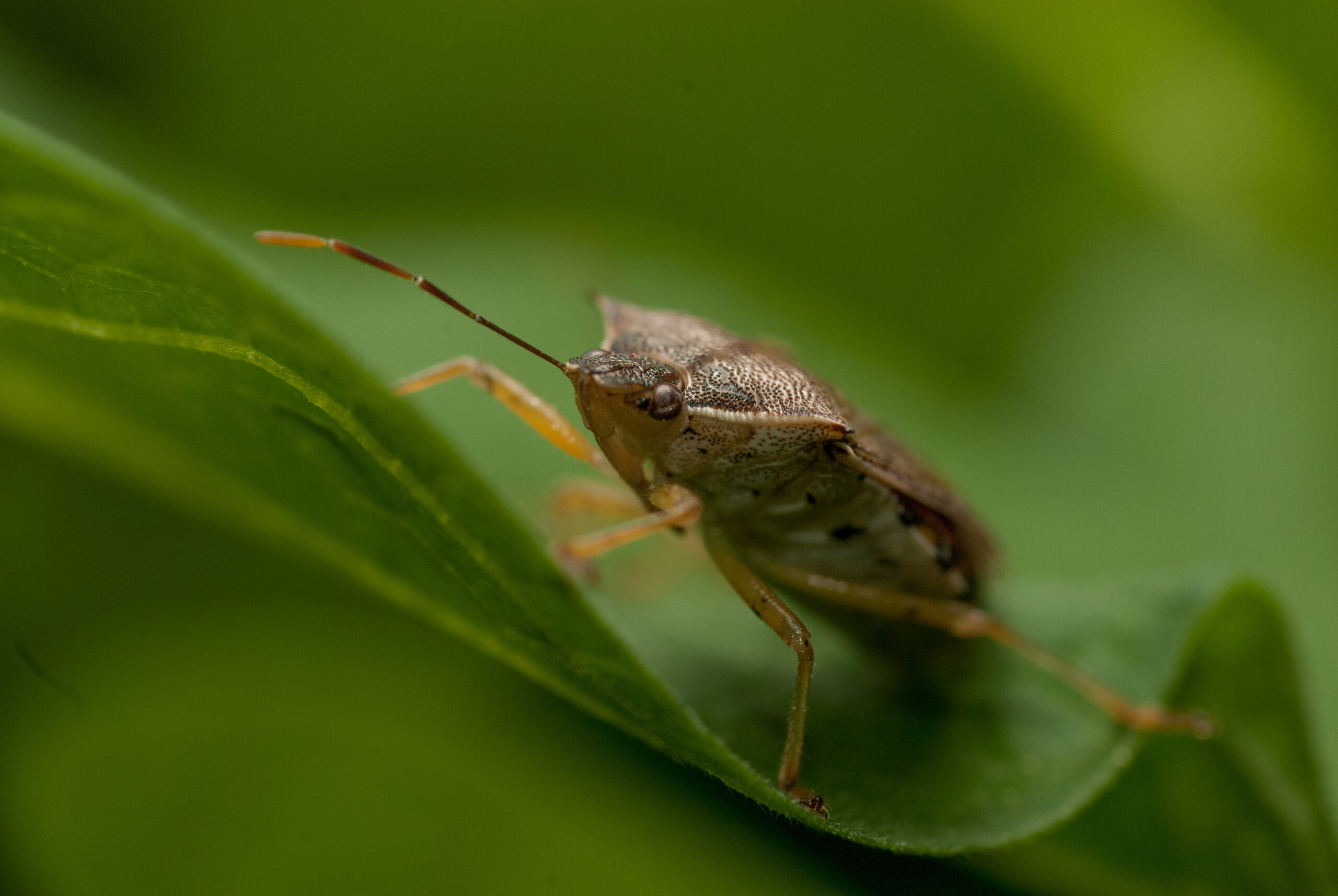








Podisus maculiventris
To order biopesticides,
please send us an email to :
please send us an email to :

Targeted crops
- Apples
- Asparagus
- Beans
- Cole crops
- Eggplant
- Potatoes
- Tomatoes
- Sweet corn
- Onions

Targeted pests
- Beet armyworms (Spodoptera exigua)
- Cabbage loopers (Trichoplusia ni)
- Cabbage worms (Pieris brassicae)
- Colorado potato beetles (Leptinotarsa decemlineata)
- Corn earworms (Helicoverpa zea)
- Diamondback moths (Plutella xylostella)
- European corn borers (Ostrinia nubilalis)
- Fall armyworms (Spodoptera frugiperda)
- Flea beetles (Alticini)
- Mexican bean beetles (Epilachna varivestis)
- Velvetbean caterpillars (Anticarsia gemmatalis)
- Western bean cutworm (Striacosta albicosta)

Application Instructions
Podisus maculiventris have a limited shelf life. They should be used as soon as possible after receipt. Ensure optimal conditions of 8-12ºC and relative humidity of 70-90%.
Distribute directly into the infested plants.
Important! Ensure that the pest insects are present in the crops before application.
Preventive application rates* generally range from 1-2 individuals per m², and 3-5 individuals per m² for light to severe infestations. Repeat introductions every 1-2 weeks, until control.
*Introduction rates may vary depending on specific crop conditions, the type of pest present, and the level of infestation.
Storage Instructions
Use upon receipt.
If needed, keep for a maximum of 7 days at 8-12°C.
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
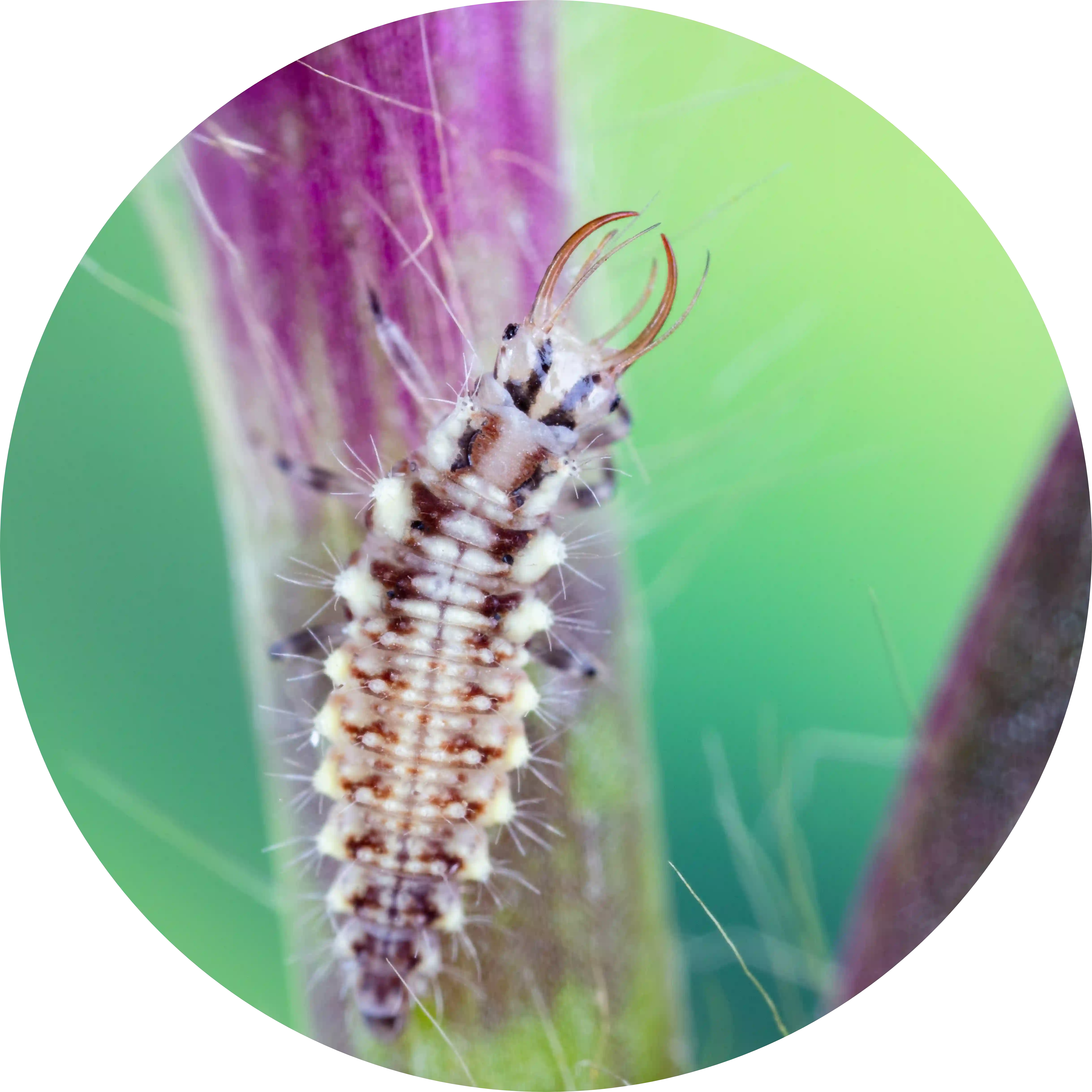
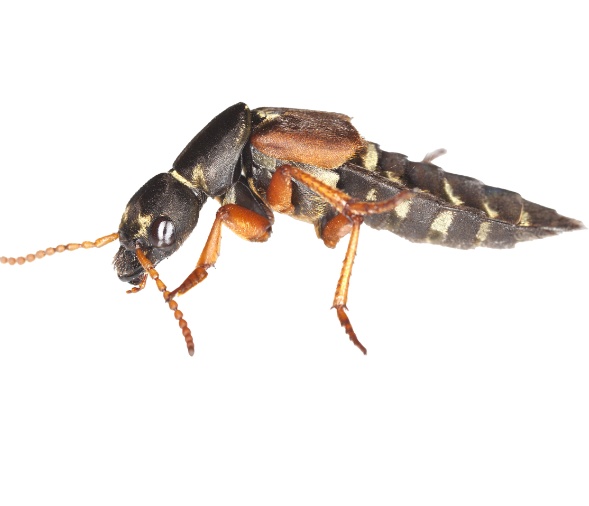








Description
The predatory stink bug Podisus maculiventris proves a powerful yet eco-friendly ally in the fight against damaging agricultural pests. This formidable natural enemy feeds mercilessly on caterpillar and beetle invaders, including the dreaded Colorado potato beetle, deploying its formidable appetite to help curb pest populations in greenhouse and open-field crops alike. By enlisting the stink bug’s aid, farmers can curb their use of synthetic pesticides and adopt greener methods of pest control, allowing for a more sustainable system of crop production. Here, the stink bug emerges as an unexpected hero—one that helps safeguard harvests through an appetite for destruction.